Secondary structure analysis using STRIED in VMD
STRIDE is a widely used secondary structure assignment tool for protein structures. This algorithm was first reported in:
Frishman D, Argos P. Knowledge-Based Protein Secondary Structure Assignment Proteins: Structure, Function, and Genetics 23:566-579 (1995)
Please also check Secondary structure analysis using DSSP.
1. Input
- STRIDE uses 3D coordinates from PDB files or MD snapshots, like DSSP.
- It looks at backbone atoms (N, Cα, C, O) as well as side-chain Cβ atoms for additional geometrical information.
2. Hydrogen bonds
- Like DSSP, STRIDE identifies backbone hydrogen bonds.
- But STRIDE uses a different energy function that accounts for bond distances and angles more explicitly.
- Hydrogen bonds are scored energetically, not just via a cutoff threshold, making it slightly more sensitive to subtle H-bond patterns.
3. Torsion angles
- STRIDE also heavily considers φ (phi) and ψ (psi) backbone dihedral angles.
- It uses probability distributions of these angles derived from high-resolution crystal structures for each type of secondary structure.
- Example: α-helix residues cluster in a particular φ/ψ region; β-strands cluster in another region.
4. Combined scoring
STRIDE assigns secondary structure based on a combined scoring function:
\[S_{total} = S_{H-bond} + S_{torsion}\]- $S_{H-bond}$ = score based on hydrogen bond energies.
- $S_{torsion}$ = score based on φ/ψ probability from known structures.
- The residue is assigned the secondary structure maximizing the total score.
5. Secondary structure types
- STRIDE assigns the same 8 standard types as DSSP (H, G, I, E, B, T, S, C).
- Because it incorporates torsion angles and probabilities, STRIDE tends to be slightly more sensitive to subtle helices or turns than DSSP.
- It also tends to give smoother assignments across residues (less “flickering” of assignments in short helices or strands).
6. Key differences from DSSP
| Feature | DSSP | STRIDE |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond detection | Electrostatic model with energy cutoff | Energy-based scoring with refined geometry |
| Torsion angles | Minor influence | Major component (φ/ψ probability) |
| Side chain atoms | Ignored | Cβ atoms used for geometry |
| Sensitivity | May miss short or distorted helices | Captures subtle helices and bends better |
| Output | 8-letter or 3-state simplified | 8-letter or 3-state simplified |
7. use STRIDE in MD trajectory
VMD has the TimeLine plugin for analyzing secondary structures via STRIDE.
Besides, check the vmd_stride.tcl in this link.
8. Comparison with DSSP
Below is an example of me using DSSP and STRIDE for a series of MD trajectory with a focus on the residue index 205:220.
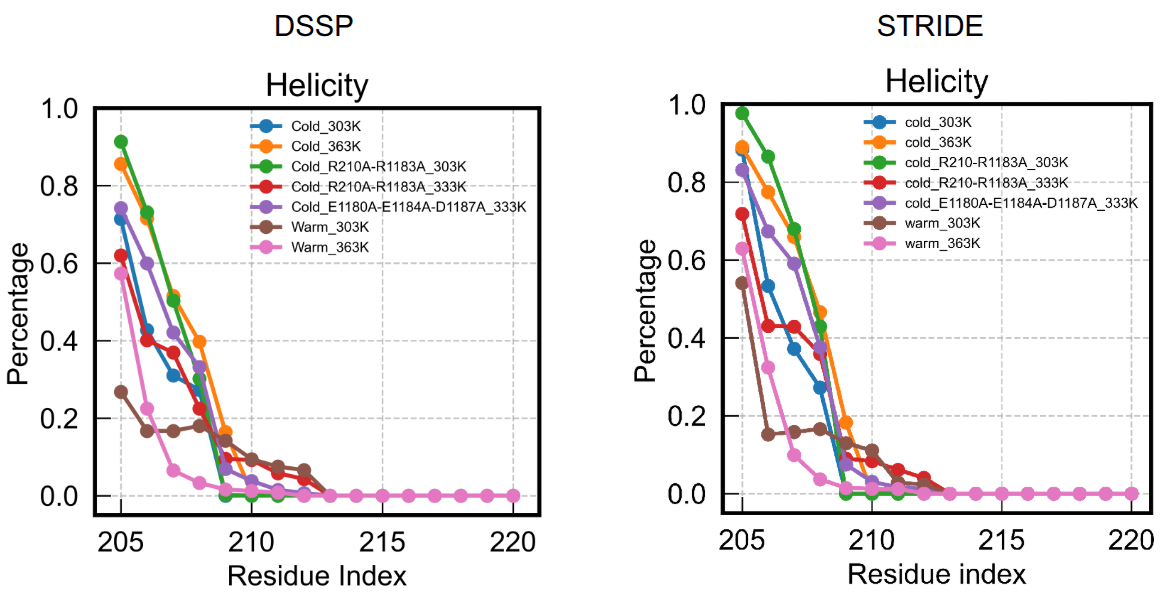
The results largely look similar, though STRIDE overall emphasizes helicity a little bit.
